Design your traceability application project with “Edge” distribution of computing power
With explanations of the different ways in which smartphones and Android mobile computers can be connected to data bases and printers on the move, design your barcode, Rfid traceability application project!
Capture, print, share, update, store!
Prerequisites: read: advantages of ruggedized scanner terminals
The Edge computing model
Mobile Edge Computing" is a model of distributed computing between mobile terminals across the network, whether private or not, using Cloud resources as little as possible, like an ERP, thus staying at the “edge” of the Cloud, which explains the term “Edge”. Terminals have their own database system, a physical or virtual display and keyboard, and above all permanent memory and super-powerful processors: that’s more than enough.
So what’s the point of Edge Computing?
They can connect to local sensors and collect measurement data, which can then be processed and, if necessary, sent to the Cloud. Analyses are produced locally, process statistics are local, and local simulations, requiring no latency (with or without an immediate network), are perfectly suited to empowering people and lightening networks and servers!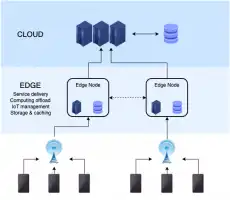
Edge structure for remote calculations on the terminal, linked to databases on lightweight servers
This data structure is well-suited to self-monitoring, self-diagnosis, easy-to-install monitoring without IT specialists, with redundancy (self-replacement of data or machines), encryption (digital signature) on-the-spot of proof data for authentication, for example.
At the end of the “Edge” process, only the data required for the Cloud, ERP or digital evidence archiving server, for example, is transmitted for storage.
Edge computing works where the action is, close to the production site, where autonomy and reactivity are required with a minimum of equipment: these are the points in common with Lean management after all.
We use all the possibilities of Edge computing in our mobile products and software: so you’ll need a minimum of networks and servers.
We’re assuming here that you know how to acquire barcode or Rfid data on your mobile and want to print, share or store it (other pages on this same site provide information on these subjects).
Different mobile data exchange architectures possible in operation
The Android terminal communicates via Wifi or 3/4/5G or BT (Bluetooth).
Here we present the different connection structures between terminals and databases for Android. We’ll go from obsolete to current modes.
Interchanges via USB: no longer used professionally except for development purposes or for very small businesses (one-person operations with no central database)!

Android interchanges via USB
First of all, USB connections with an Android are useful for loading programs (Apk) on certain smartphones: this is the only use for this mode, although it can be done by scanning the QRcode of the apk address. But on some ruggedized terminals, there are no longer any USB connectors, so this mode, inherited from the old Windows CE world, can no longer be used in “operating” mode.
So we’re moving on to mobile network connections:.
- Wifi for “indoor” applications indoors or close to premises
- 3/4/5G for outdoor mobile applications.
Wifi-4G exchanges on Excel/CSV databases: discontinued for security reasons.
The database is an Excel / csv file, stored on a PC linked by IP: here exchanges are limited to a single direction: either a reading of the table (parameters) by the terminal, or an addition of lines in another (entered data). This system is even more limited when there are several terminals connected: it’s low-cost in terms of maintenance and is reserved for a few cases with no future development, and it is strictly forbidden by Windows for security reasons. So no longer used.
Wifi- 4G exchanges on SQL / NoSQL databases or via API: recommended.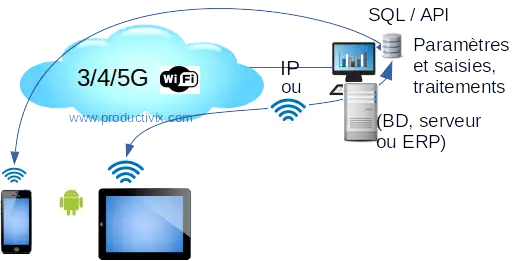
Mobile IP connections with SQL/NoSQL databases via API
The database is of the SQL / NoSQL type, or can be accessed by an ERP via API: depending on rights, exchanges can be read and write, with non-competing access processes to data modifications: ideal for professional working structures on mobile terminals. Edge computing" can then be carried out on the terminal: calculations and results can be displayed in addition to traditional data collection.
Now that we’ve finished with data entry, let’s move on to printing on labels or receipts:
Possible mobile data printing architectures: receipts or labels, reports
There are two possible modes: Bluetooth (BT) or Wifi / IP direct, the USB mode connected to the PC is not easily accessible from a mobile terminal: so we won’t talk about it: but beware of your purchases if they are made upstream of the project, these USB machines alone will be unusable!
BT printing: the most personal of all
Personal mobile printer to terminal connection mode: via Bluetooth
BT printing is generally reserved for mobile printers worn on a belt, close to the operator’s hand. Receipts or self-adhesive labels with barcodes or Rfid tags can be printed. The data to be printed is sent via the BT of the rugged smartphone carried by the operator. Table-top printers connected by BT are also conceivable: this is reserved for nearby terminals.
Printing by wifi / IP: the most shared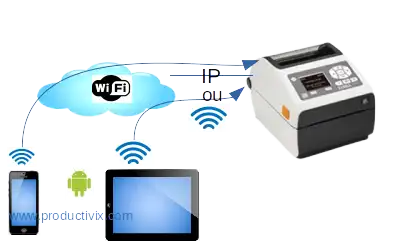
shared label printer connection mode to mobile terminals: via IP (fixed) wired or Wifi
The printer (office or industrial) is connected to a network via an Ethernet cable (fixed IP) or Wifi, so it’s shared and data is sent via the terminals. In general, only one label format is used per machine, so there are no surprises when printing after a format change.
Now you know everything: contact us for your project!
